
Shweyoe Dictionary
Shweyoe Dictionary (English, Russia, Korea, Japan, Thai to Myanmar). Please click here to download.

Shweyoe Dictionary (English, Russia, Korea, Japan, Thai to Myanmar). Please click here to download.

Lightshot is one of open source screenshot software for Windows and Mac. In this software, you can save as jpg, png, etc...,. And you can also edit and make remarks. If you want to download it, please click here.

Please click here to download Myanmar Font for Viber. And then, follow the below instructions:
1. Press Windows and R keys together
2. Type fonts in the run box.
3. Copy and paste Myanmar Font you've downloaded.
4. Then restart your computer.


Cisco certifications are one of the famous certifications in networking field.
This is all bout Cisco Certifications for brothers and sisters who are trying to take Cisco exams. If you want to learn, click here.

There are four octet in IPV4. Each octet has 8 bits. So, there are 32 bits in IPV4. IPV4 is based on binary (0, 1) and decimal (0 to 9).
| First Octet | Second Octet | Third Octet | Fourth Octet |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 bits | 8 bits | 8 bits | 8 bits |
| 2726252423222120 | 2726252423222120 | 2726252423222120 | 2726252423222120 |
| 255.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.255 |
How to become 255.255.255.255 ? As each octet has 8 bit and is based on binary.... 27 = 128, 26 = 64, 25 = 32, 24 = 16, 23 = 8, 22 = 4, 21 = 2, 20 = 1 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 255
| Decimal | = | Binary | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Octet | 2nd Octet | 3rd Octet | 4th Octet | | 1st Octet | 2nd Octet | 3rd Octet | 4th Octet | ||||||||||
| 192 | . | 168 | . | 1 | . | 0 | | 11000000 | . | 10101000 | . | 00000001 | . | 00000000 |
Let's explore 192.168.1.0/24.... Network Address = 192.168.1.0 Subnet Mask = 255.255.255.0 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.255
Let's explore 192.168.1.0/25.... 1nd Network Address = 192.168.1.0 Subnet Mask = 255.255.255.128 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.127 2nd Network Address = 192.168.1.128 Subnet Mask = 255.255.255.128 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.255
Let's explore 192.168.1.0/26... 1st Network Address = 192.168.1.0 Subnet Mask = 192.168.1.192 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.62 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.63 2nd Network Address = 192.168.1.64 Subnet Mask = 192.168.1.192 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.127 3rd Network Address = 192.168.1.128 Subnet Mask = 192.168.1.192 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.190 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.191 4th Network Address = 192.168.1.192 Subnet Mask = 192.168.1.192 Usable IP Addresses = 192.168.1.193 to 192.168.1.254 Broadcast Address = 192.168.1.255 (Note: The Subnet Mask is reverse proportional to host range. The larger the subnet mask, the smaller the host range.)
The following table is formula for Ipv4 addresses (Class C). I've made it when I was in Singapore Polytechnic.
| Binary | Decimal | Prefix | Subnet Mask | Count of Networks | Usable IP Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | /24 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 | 254 |
| 27 | 128 | /25 | 255.255.255.128 | 2 | 126 |
| 26 | 64 | /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 4 | 62 |
| 25 | 32 | /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 8 | 30 |
| 24 | 16 | /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 16 | 14 |
| 23 | 8 | /29 | 255.255.255.248 | 32 | 6 |
| 22 | 4 | /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 64 | 2 |

The networking devices need IP addresses to communicate with each other on the network. There are two types of IP addresses versions: IP Version 4 (IPv4) and IP Version 6 (IPv6).
IPv4 Address
In IPv4 address, the host can communicate in one of three different ways:
Unicast: The process of sending a packet from one host to an individual hos
Broadcast: The process of sending a packet from one host to all hosts in the network
Multicast: The process of sending a packet form one host to selected group of hosts
In IPv4, the network range is defined by the followings:
Network address: A special network that refers to the network
Subnet Mask The subnet mask is a 32-bit values used with IPv4 address that specifies the network portion of the address to the network device. The subnet mask uses 1s and 0s to indicate which bits of the IPv4 address are network bits and which bits are hosts bits.
Host address: The unicast address assigned to the end device in the network
Broadcast address: A special address used to send data to the all hosts in the network
For Example,
Network Network Address Subnet Mask Host Range Broadcast Address
192.168.1.0/24 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 to 254 192.168.1.255
192.168.2.0/25 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.128 192.168.2.1 to 126 192.168.2.127
IPv4 Network Classes
Address Classes First Octet Range Prefix and Mask Number of Possible Networks Number of Hosts
A 1 to 127 /8 255.0.0.0 126 16,777,217
B 128 to 191 /16 255.255.0.0 16,382 65,534
C 192 to 223 /24 255.255.255.0 2,097,159 254
IPv4 Public and Private Addresses
Although most IPv4 addresses are public addresses designated for use in networks that are accessible on the Internet, there are blocks of addresses used in network that are not accessible on the Internet. These addresses are called private addresses.
The private address blocks are:
Class A 10.0.0.0/8 (10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255)
Class B 172.16.0.0/12 (172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255)
Class C 192.168.0.0/16 (192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255)
Multicast Addresses 224.0.0.0/4 (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255)
The multicast transmission is designed to conserve the bandwidth of IPv4 network. It reduces the traffic by allowing a host to send a single packet to a selected set of hosts. To reach multiple destination hosts using unicast communication, a source host would need to send an individual packet addressed to each host. With multicast, the source host can send a single packet that can reach thousands of destination hosts.
Experimental Addresses 240.0.0.0/4 (240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254)
These addresses are reserved for future use. This suggests that they could be converted to usable addresses. Currently, these addresses are not usable in IPv4 network. However, these addresses are used for research.
Default Route 0.0.0.0/8 (0.0.0.0 to 0.255.255.255).
The default route is “catch all” route to route packets when the specific route is not available.
Loopback Address 127.0.0.0/8 (127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255).
The loopback address is special address that hosts use to direct traffic to themselves.
Link-Local Addresses 169.254.0.0/16 (169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255)
These link-local addresses can be automatically assigned to the local host by the operating system in environment where no IP configuration is available.
Test-Net Addresses 192.0.2.0/24 (192.0.2.0 to 192.0.2.255)
The test-net-addresses are set aside for teaching and learning purpose.

LAN (Local Area Network)
LAN is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building and has its network equipment and interconnects locally managed.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN is the network that is interconnected by two or more LANs. WAN is not only defined by a larger geographic distance, but also generally defined by leased telecommunication circuits.

Network Protocols are machine languages used to communicate the devices on the network. For devices to communicate on a network, they must follow different protocols that perform the many tasks to be complicated. The protocols define the followings:
- The format of the message, such as how much data to put into each segment
- The way intermediary devices share information about the path to the destination
- The method to handle update messages between intermediary devices
- The process to initiate and terminate communications between hosts
The examples of Network Protocols are as follows:
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): HTTP is a common protocol that controls the way that a web server and web client interact.
Transport Protocol: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is the transport protocol that manages the individual conversions between a web server and web client. TCP divides the HTTP messages into smaller pieces, called segment, to be sent to the destination client. It also controls the size and rate of messages exchanged between the server and the client.
Internet Protocol (IP): IP takes the formatted segments from TCP, encapsulates them into packets, assign the appropriate addresses, and select the best path to the destination client.
Network Access Protocols: Network access protocols describe two primary functions: data-link management and the physical transmission of data on the media. Data-link management protocols take the packets from IP and format them to be transmitted over the media. The physical media controls how the signals are sent over the media and how they are interpreted by the receiving clients.

OSI Model
The Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model provides an abstract description of the network communication process. International Organization for Standard (ISO) develops it to provide a road map for non-proprietary protocol development. The OSI model is just a reference model and many of OSI protocols are no longer in use. There are seven layers in OSI Model. Those are as follows:
Layer 7 - Application
Performs services for the application used by the end users.
Layer 6 - Presentation
Provides data format information to the application.
Layer 5 - Session
Manages session between users.
Layer 4 - Transport
Defines data segments and numbers them at the source, transfers the data, and reassembles the data at the destination.
Layer 3 - Network
Creates and addresses packets for end-to-end delivery through intermediary devices in other network.
Layer 2 - Data Link
Creates and addresses frames for host-to-host delivery on the local LANs and between WAN devices.
Layer 1 - Physical
Transmits binary data over media between devices. Physical layer protocols define media specifications.
TCP/IP Model
TCP / IP is an open standard. The rules and implementation of the TCP/IP model were cooperatively developed by members of the industry using Request for Comments (RFC) documents. There are four layers in TCP/IP Model. Those are as follows:
Layer 4 - Application
Represents application data to the user.
Layer 3 - Transport
Supports communication between devices and performs error correction.
Layer 2 - Internet
Finds the best path through the network.
Layer 1 - Network access
Controls hardware devices and media.
Comparison of OSI and TCP / IP Model
| 7. Application | 4. Application |
| 6. Presentation |
|
| 5. Session |
|
| 4. Transport |
3. Transport |
| 3. Network | 2. Internet |
| 2. Data Link | 1. Network Access |
| 1. Physical |

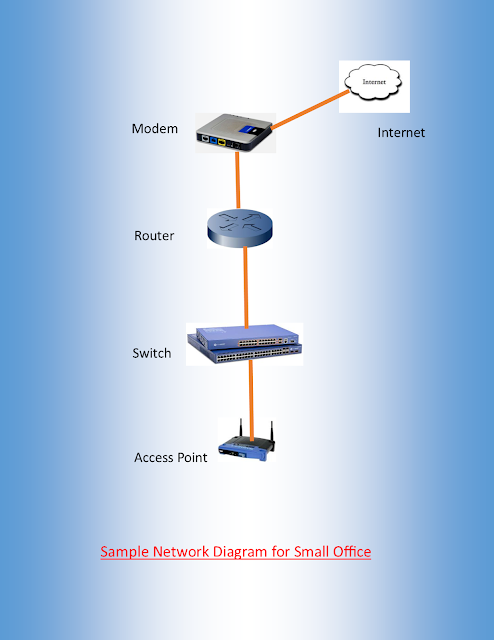
Access Point
Normally, the access points allow the users to connect the Internet through the Wired Network(Switch, Router, Modem, etc....).
Switches
The switch (layer 2) normally receive the packets, process it and forward data to the destination.
Routers
Normally, the router is used to connect the different networks. But there are so many router functions if detailed.
Modem
The Modem is the common networking device that turns the digital data of an electronic device into modulated electrical signal for transmission over telephone lines and demodulated by another modem at the receiver side to recover the digital data.
Internet
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that use the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) to link billions of devices worldwide.

Desktop Computer
A common computer used in a home or offices.
Laptop
A portable computer.
LAN Media
Local-area network media, usually copper cable.
Wireless Media
Depicts local-area network wireless access.
Switch
The most common devices for interconnecting local-area networks
Router
A device that helps direct message between networks
Firewall
A device that provides security of network.
Server
A common computer dedicated to provide application services to end users on a network. Server stores information to share with its clients.
Cloud
A group of networking devices out of local management control, often the Internet itself.

The example of how to configure the Frame Relay in Cisco Networking Devices is shown in the below with the picture together. I hope this example will be benefit for brothers and sisters who are learning Cisco Networking.
Router 1
en
config t
hostname R1
int g0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int s0/0/0
description Link From Router1 to Router2
ip address 223.128.1.1 255.255.255.252
encap frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay interface-dlci 101
no shut
int s0/0/1
encap frame-relay
no shut
exit
int s0/0/1.201 point-to-point
description Link From R1 to R3
ip address 223.128.1.5 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 201
no shut
exit
int s0/0/1.301 point-to-point
description Link From R1 to R4
ip address 223.128.1.9 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 301
no shut
exit
int s0/0/1.401 point-to-point
description Link From R1 to R5
ip address 223.128.1.13 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 401
no shut
exit
int s0/0/1.501 point-to-point
description Link From R1 to R6
ip address 223.128.1.17 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 501
no shut
exit
router rip
version 2
network 192.168.1.0
network 223.128.1.0
network 223.128.1.4
network 223.128.1.8
network 223.128.1.12
network 223.128.1.16
end
copy run start
Router 2
en
config t
hostname R1
int g0/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int s0/0/0
description Router2 to Router1
ip address 223.128.1.2 255.255.255.252
encap frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay interface-dlci 102
no shut
exit
router rip
version 2
network 192.168.2.0
network 223.128.1.0
end
copy run start
Router 3
en
config t
hostname R3
int g0/0
description Link From Router3 to Router1
ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int s0/1/0
description Link From Router3 to Router1
ip address 223.128.1.6 255.255.255.252
encap frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay interface-dlci 103
no shut
exit
router rip
version 2
network 192.168.3.0
network 223.128.1.4
end
copy run start
Router 4
en
config t
hostname R4
int g0/0
ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int s0/1/0
description Link From R4 to R1
ip address 223.128.1.10 255.255.255.252
encap frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay interface-dlci 104
no shut
exit
router rip
version 2
network 192.168.4.0
network 223.128.1.8
end
copy run start
Router 5
en
config t
hostname R5
int g0/0
ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int s0/0/0
description Link From Router5 to Router1
ip address 223.128.1.14 255.255.255.252
encap frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay interface-dlci 105
no shut
exit
router rip
version 2
network 192.168.5.0
network 223.128.1.12
end
copy run start
Router 6
en
config t
hostname R6
int g0/0
ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int s0/1/0
description Link From Router6 to Router1
ip address 223.128.1.18 255.255.255.252
encap frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay interface-dlci 106
no shut
exit
router rip
version 2
network 192.168.6.0
network 223.128.1.16
end
copy run start
***Thank You***